Detailed Explanation of Negative Pressure Drainage Bottles and Their Production Equipment - High-frequency Welding Machine
Introduction
In modern medicine, negative-pressure drainage technology has been widely adopted in surgical and therapeutic procedures, demonstrating remarkable effectiveness in wound drainage and dressing changes for patients with trauma, tumors, inflammation, and other conditions. As the core component of negative-pressure drainage systems, the quality and performance of negative-pressure drainage bottles directly impact patient safety and treatment outcomes. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the working principles, structural features, and production equipment—specifically high-frequency welding machines—for negative-pressure drainage bottles, aiming to offer valuable insights for research and manufacturing in related fields.
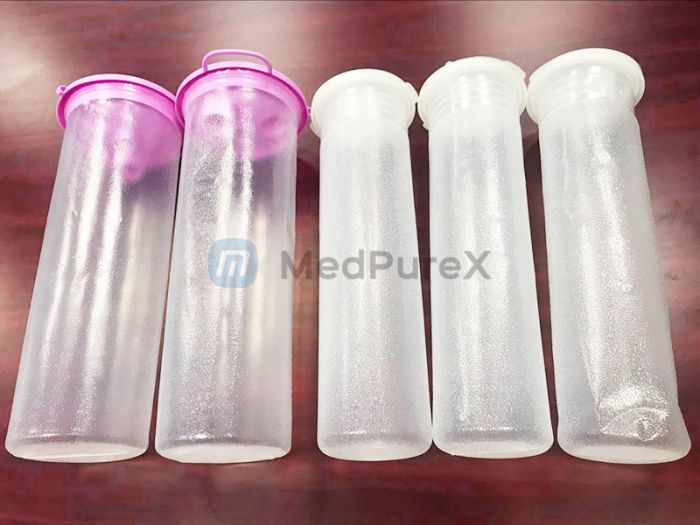

I. Working Principles and Structural Features of Negative-Pressure Drainage Bottles
-
Working Principles
A negative-pressure drainage bottle utilizes a vacuum pump to create a negative pressure gradient. Connected to a suction device via tubing, it facilitates drainage and dressing changes for wounds or affected areas. When the bottle is attached to the suction device, the vacuum pump evacuates air from the container, generating a negative pressure gradient. This gradient directs fluid from the wound or lesion outward, achieving drainage. During dressing changes, new dressings placed within the bottle automatically adhere to the wound through this negative pressure, simplifying medical procedures. -
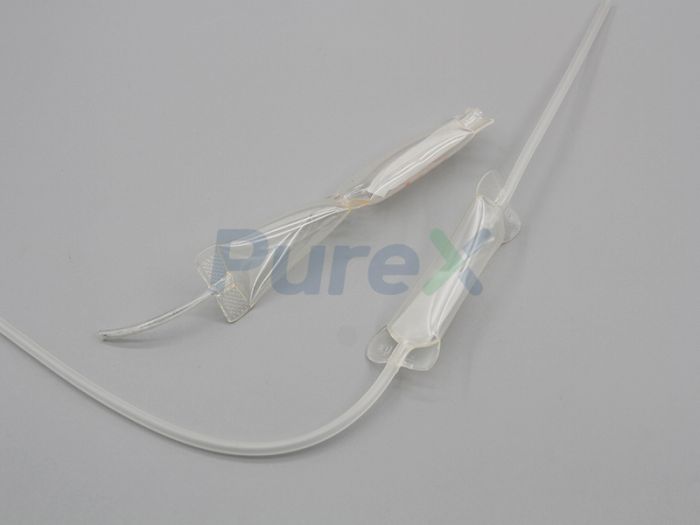
Structural Features
The negative-pressure drainage bottle consists of the following key components:
- Bottle body: Cylindrical design with liquid inlet and outlet at the base.
- Sealing ring: Ensures airtightness.
- Suction tip: Conical shape for compatibility with tubing of varying diameters.
- Filter: Removes impurities from drained fluid.
- Liquid level indicator: Monitors fluid volume in real time.
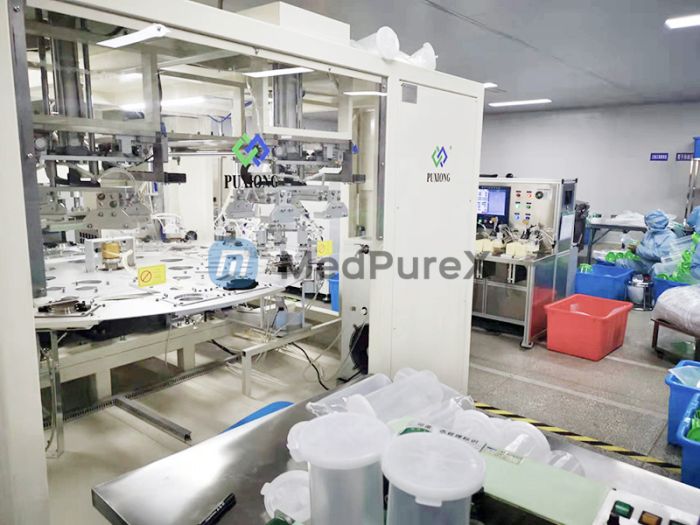
II. High-Frequency Welding Machines in Negative-Pressure Drainage Bottle Production

-
Working Principles of High-Frequency Welding Machines
High-frequency welding machines employ high-frequency currents to instantaneously heat metal materials to a molten state, followed by applied pressure to fuse them. In bottle production, this process enhances sealing performance and tensile strength.

-
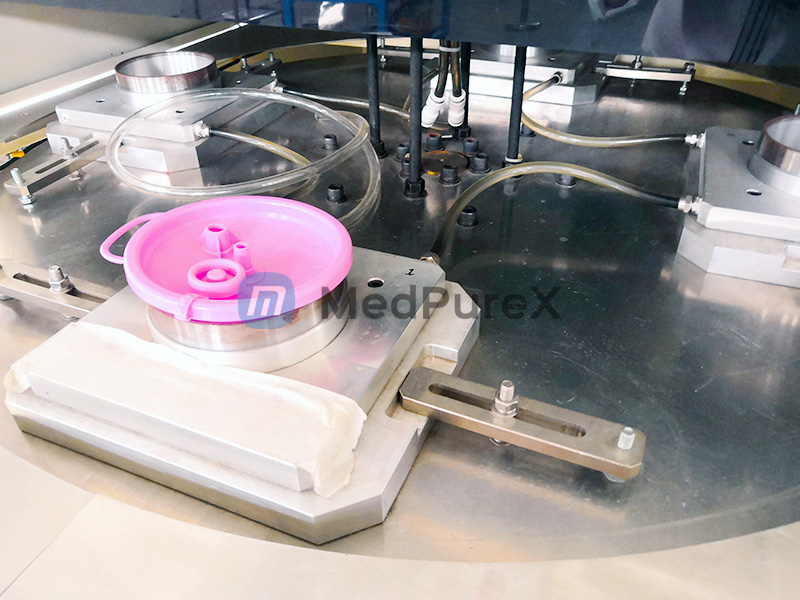
Structural Features of High-Frequency Welding Machines
The machine comprises:
- Power module: Provides stable voltage and current.
- Induction coil: Generates a high-frequency electromagnetic field to heat workpieces.
- Workpiece clamp: Secures the bottle during processing.
- Cooling system: Prevents overheating and deformation.
- Control system: Automates operational parameters.
- Operational Guidelines
Step-by-step process: - Secure the bottle in the workpiece clamp.
- Position the induction coil against the bottle surface, eliminating air gaps.
- Activate the machine, adjusting current intensity and heating duration for optimal thermal distribution.
- Apply pressure to fuse metal components, completing the welding process.
Key considerations: Strictly control temperature and heating duration to prevent deformation or damage.
Conclusion
As the cornerstone of negative-pressure drainage systems, the quality and functionality of drainage bottles are critical to patient safety and therapeutic efficacy. This article elucidates the technical and manufacturing aspects of negative-pressure drainage bottles and their production equipment, offering foundational insights for industry stakeholders. With advancements in medical technology, these devices are poised to play an increasingly vital role in diverse clinical applications