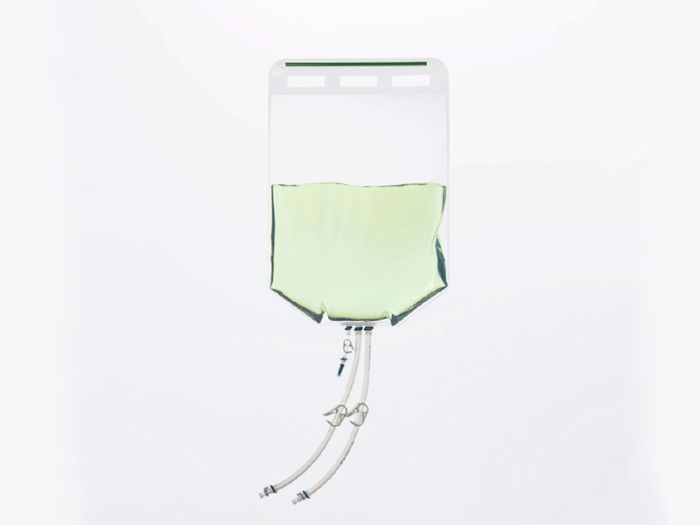
The liquid bag is welded and cut in one step to form
The integrated welding and cutting one-step molding process is a highly efficient and precise liquid bag manufacturing technique. By merging welding and cutting into a single automated procedure, this method significantly enhances production efficiency while ensuring product quality. Below is a detailed analysis of its core principles:
.jpg)
1. Process Principles
Material Layering and Alignment
- Multi-layer composite films (e.g., PE/PA/PE structure) are used as the base material.
- Films are unwound via a pay-off system and precisely aligned.
- A tension control system ensures flatness, avoiding wrinkles or misalignment during welding.
Synchronized High-Frequency Welding and Cutting
- High-Frequency Welding: Utilizes high-frequency electromagnetic fields to polarize film molecules, generating heat under pressure to form sealed welds. Temperature, pressure, and duration are precisely controlled by PLC, ensuring weld strength ≥ substrate material.
- Ultrasonic Cutting: Upon welding completion, an ultrasonic transducer generates high-frequency vibrations. A cutting die slices the film while melting the edges to seal the切口, preventing fiber shedding or leakage.
Integrated Forming
- Welding and cutting are driven by a single servo motor, synchronized via belts or gears to ensure precise alignment of weld seams and cut lines. This minimizes post-processing errors.
2. Technical Advantages
Enhanced Efficiency
- Traditional methods require 30–60 seconds per piece for separate welding and cutting steps. The one-step process reduces this to 5–10 seconds, boosting efficiency by 5–10x.
Consistent Quality
- Automation eliminates human error:
- Weld strength uniformity ≥ 95%.
- Cutting dimensional tolerance ≤ ±0.5 mm.
- Sealing performance passes helium leak tests (leakage rate ≤ 1×10⁻⁶ mbar·L/s), meeting food/pharmaceutical-grade requirements.
Cost Optimization
- 40% reduction in floor space for equipment.
- 30% lower energy consumption per unit.
- Scrap rate drops from 3–5% (traditional) to <0.5%, with material utilization reaching 98%.
3. Applications
Medical Sector
- Production of infusion bags and dialysis solution bags.
- Welds are non-toxic and residue-free, compliant with USP Class VI biocompatibility standards.
4. Key Equipment Selection Criteria
High-Frequency Welding Machine
- Power range: 5–20 kW (based on film thickness).
- Frequency: 13.56 MHz or 27.12 MHz.
Synchronized Cutting System
- Power: 2000–4000 W; Frequency: 20 kHz or 40 kHz.
- Cutting die: Titanium or carbide alloy, blade angle 30°–45°, ensuring smooth cuts.
Automation Control System
- Equipped with an HMI touchscreen supporting multi-language operation and parameter storage.
- Integrated vision inspection for real-time monitoring of weld quality and cut dimensions.


.jpg)