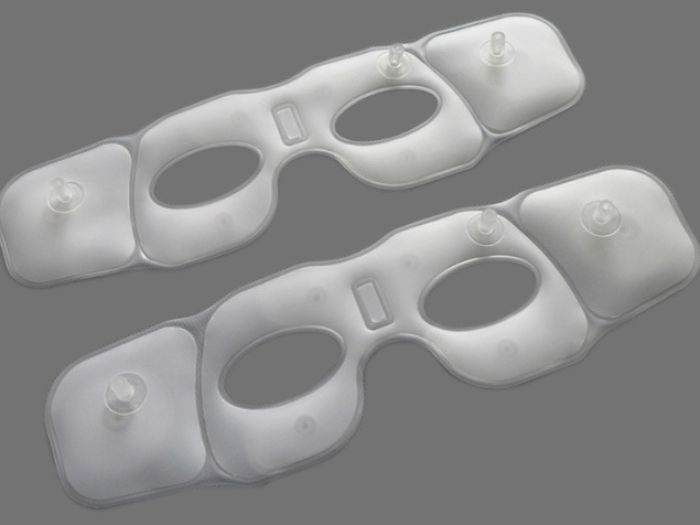
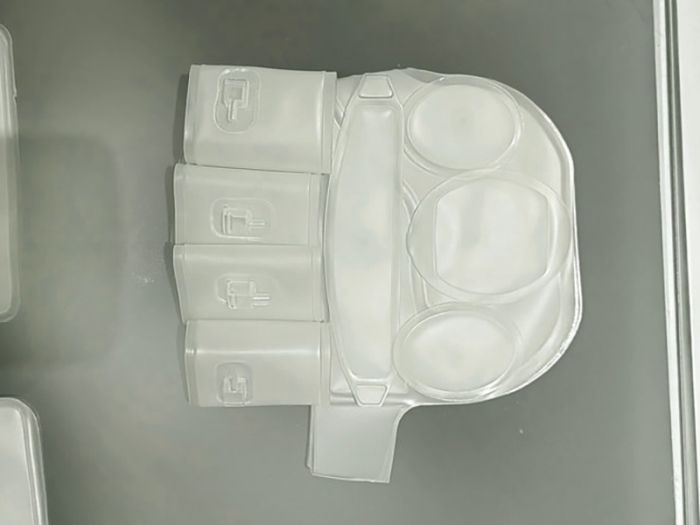
Anorectal pocket formation
An ostomy pouch is a medical device designed to collect bodily waste, such as urine or feces.
I. Classification
Ostomy pouches are generally categorized into three types:
-
Closed-End Pouches
Suitable for users requiring pouch replacement no more than once daily. -
Drainable Pouches
Designed for semi-formed or liquid stool, allowing frequent emptying as needed. -
Urostomy Pouches
Specifically for urine and liquid drainage, equipped with an anti-reflux valve and compatibility with drainage bags.

By Application:
- Single-Use Pouches
- Double-Use Pouches
By Design:
-
One-Piece Systems
Typically disposable with pre-cut openings for ease of use, ideal for dexterous users or the elderly. -
Two-Piece Systems
Feature separable pouches and adhesive bases, enabling base retention during pouch changes. Benefits include:- Skin protection around the stoma.
- Customizable base cutting to match stoma size.
- Floating flange design to avoid abdominal pressure.
Note: Not recommended for patients with stoma prolapse, parastomal hernias, or peristomal凹陷 (use convex bases for recessed stomas).
II. Materials
-
Co-Extruded Film
Made from multi-layer PE (high-barrier), EVA, or TPE films, offering:- Soft texture and superior odor resistance.
- Biocompatibility and antimicrobial properties to reduce infection risks.
- Durability and wear resistance for long-term use.
-
Silicone
A flexible, durable organic material with:- Excellent biocompatibility and antimicrobial performance.
- Superior sealing to prevent leaks.
Drawback: Limited breathability, which may cause skin irritation or eczema.
Ideal for chronic conditions (e.g., diabetes) requiring long-term comfort.
III. Applications
Ostomy pouches are widely used in medical settings for patient care, including:
-
Urinary Incontinence
Collect urine/feces to minimize contamination of clothing and surroundings. -
Gas Relief
Assist patients with intestinal obstruction or post-surgery gas drainage. -
Constipation Management
Facilitate stool collection and support complementary therapies (e.g., medication, dietary adjustments). -
Hernia Repair
Post-surgical use with synthetic mesh implants to prevent abdominal contamination. -
Radiation Therapy
Manage secretions from skin ulcers caused by cancer radiotherapy.
IV. Production Process
Manufacturing scales vary based on output demands:
- Automated High-Frequency (HF) Equipment
- Semi-Automated HF Systems
Recommended: Puxiong Group’s Four-Station Rotary Heat Sealing Machine- Integrates sealing and cutting in one step for precision and strength.
- Automated four-station cycle enhances efficiency.
- PLC control system for accuracy, user-friendliness, and multi-recipe storage.
- Versatile for diverse medical products via mold changes, maximizing ROI.